PostgreSQL ASCII() Function
The PostgreSQL ASCII() function returns an ASCII code value of a character. In the case of UTF-8, the ASCII() function returns the Unicode code point of the character.
Syntax
The following illustrates the syntax of ASCII function:
ASCII(char)Arguments
The ASCII() function requires one argument:
1) char
The char argument is a character that you want to get the ASCII code.
If you pass a string to the ASCII() function, it will return the ASCII code of the first character.
Return value
The ASCII() function returns an integer that represents the ASCII code value of the input character. In the case of a UTF-8 character, it returns an integer which is corresponding to the Unicode code point.
Examples
The following example uses the ASCII() function to get the ASCII code values of the character A and a:
SELECT
ASCII( 'A' ),
ASCII( 'a' );The output is:
 If you pass a sequence of characters to the
If you pass a sequence of characters to the ASCII() function, you will get the ASCII code of the first character as shown in the following example:
SELECT
ASCII( 'ABC' );The function returns the ASCII code of the letter A which is 65 as follows:
 The following example illustrates how to use the
The following example illustrates how to use the ASCII() function to get the Unicode code point of a UTF-8 character:
SELECT
ASCII( 'Ω' );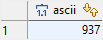
Remarks
To get the ASCII code value or Unicode code point of an integer, you use the CHR() function.
In this tutorial, you have learned how to use the PostgreSQL ASCII() function to get the ASCII code or Unicode code point of a character.